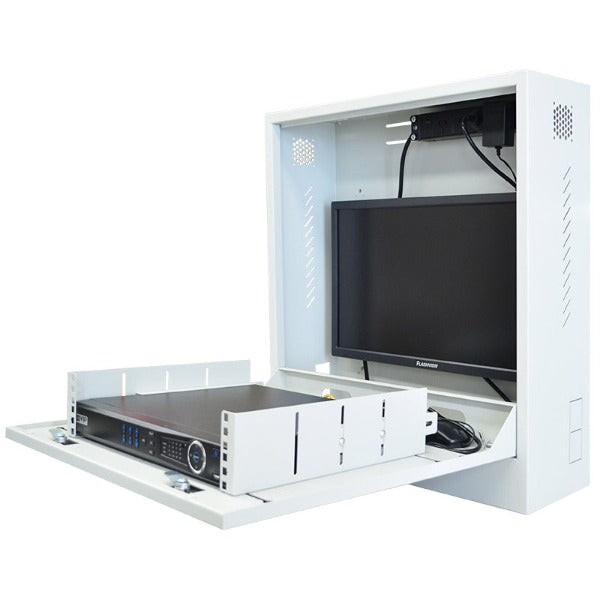
While both NVRs and DVRs are used for video recording, the main difference lies in the type of cameras they support. NVRs work with IP cameras that transmit video data over a network (usually Ethernet), whereas DVRs are designed to work with analog cameras that transmit video signals via coaxial cables.
NVRs offer several advantages, including support for high-resolution video, scalability (easy to add more cameras), remote access and management via network connectivity, advanced features like motion detection and video analytics, and compatibility with modern IT infrastructure.
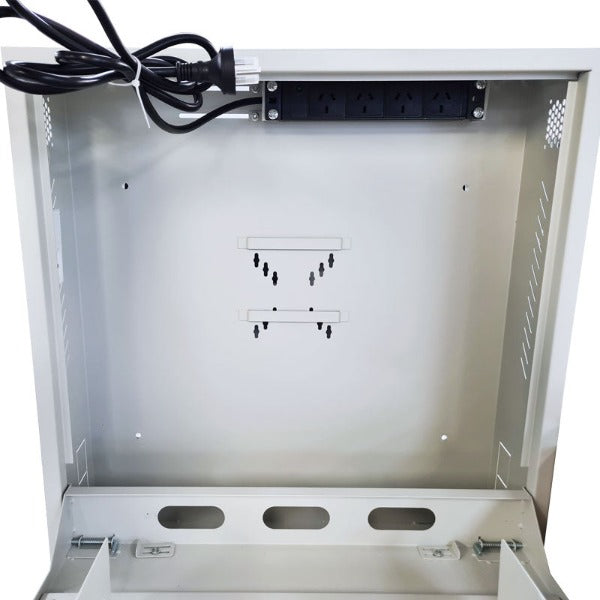
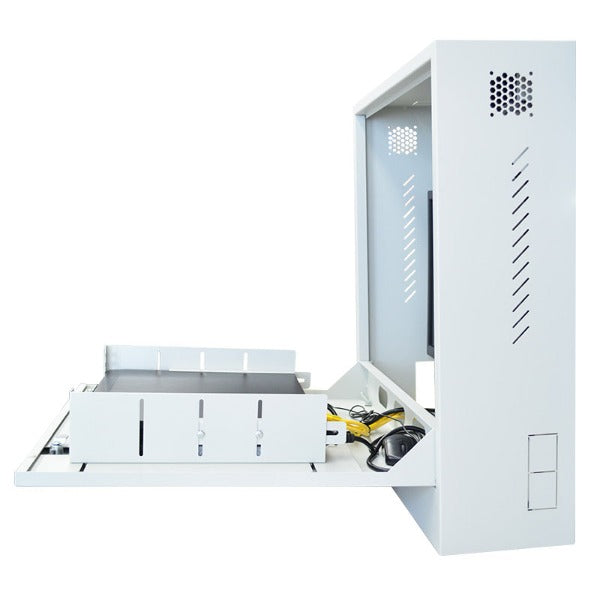
Setting up an NVR system involves several steps: connecting IP cameras to the NVR via Ethernet cables, configuring network settings, setting up recording parameters (such as resolution, frame rate, and compression), and configuring user access permissions. Some NVRs also require additional configuration for remote access and integration with other systems.
NVRs typically support various types of storage, including internal hard drives, external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), and cloud storage. The choice of storage depends on factors such as capacity requirements, redundancy needs, and budget considerations.
At CTC Communications are hard drive storage size is listed in the product, additional hard drives can also be purchased.
Yes, most NVRs offer remote access capabilities, allowing users to view live or recorded video footage from anywhere with an internet connection. This is typically done through a web interface or dedicated mobile app provided by the NVR manufacturer.
Many NVRs support integration with third-party devices and software, such as access control systems, alarm systems, and video management software (VMS). This enables users to create comprehensive security solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Security is a critical consideration for NVR systems, especially since they handle sensitive video data. To enhance security, NVRs often support encryption protocols, user authentication mechanisms, and network security features such as VPNs and firewall integration. It's essential to follow best practices for cybersecurity when deploying and configuring NVR systems.
Maintenance tasks for NVRs typically include regular software updates to patch security vulnerabilities and add new features, monitoring system health and performance, checking storage capacity and integrity, and ensuring the physical security of the NVR device itself.
When choosing an NVR, consider factors such as the number of cameras supported, recording resolution and frame rate, storage capacity and scalability, network connectivity options, compatibility with existing infrastructure, ease of use, available features (such as motion detection and remote access), and vendor support and reputation.